How was the visit of a rich Roman? A new research project has attempted to remodel the interior of one of the many luxury homes in the Roman city of Pompeii.
Pompeii and Herculaneum were buried in AD 79. Due to the massive eruption of Vesuvius, near present-day Naples in Italy.
The volcanic eruption closed the city in a glimpse into Roman daily life nearly 2,000 years ago. This daily life is well documented through, among other things, graffiti, which is both political and lively at the same time.
Pompeii was clearly a prosperous city, and many luxurious homes and valuables were discovered here after more than a hundred years of excavations.
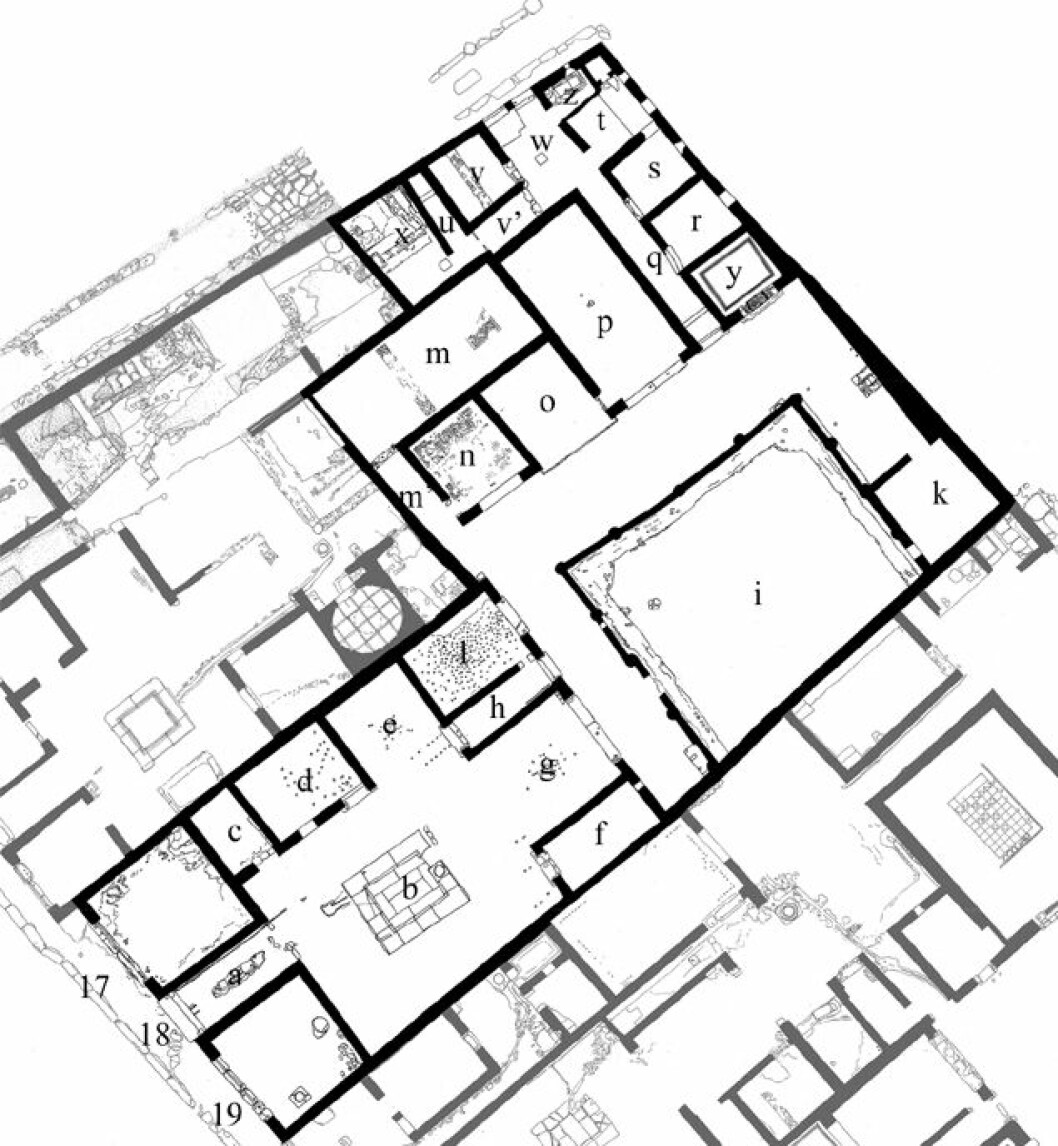
One of these luxury homes is called House of Greek Epigrams, or “the house that contains the Greek word.” A vignette is a short poem that often describes a person.
The house has been recreated in virtual reality, among other things to investigate how guests experience the house when they visit.
The research was described in the journal Antiquity.

Greek inscriptions
The researchers behind the project work at Lund University in Sweden. They have long worked on a research project on various aspects of Pompeii and Roman culture.
The researchers built the house in the Unity game engine, and the participants can move around the house using virtual reality glasses.
At the same time, the subjects’ eyes were monitored so that the researchers could measure where the subjects fixed their eyes inside the home. The study of antiquity is a technical description of the system, but the goal is to reveal more knowledge about why the Romans built their homes as they did.
Digert
The VR reconstructed house consists of approximately 30 rooms and a corridor, and the house itself may have been made by several condominiums that were combined once before the volcano eruption in the year 79. The house is part of what is called an insula. It is a Roman neighborhood with apartments and buildings.
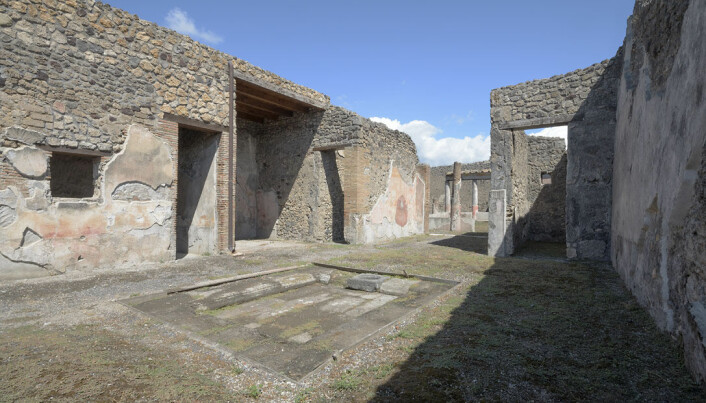
The house should be rich in murals in several rooms and gardens within the walls. The researchers do not know the purpose for which all the rooms were used, but they do mention several dining rooms and rooms for servants.
The house also had a large atrium – an open room that was richly decorated. It also has a pool in the middle that collects rainwater from the hole in the roof.
The house was first excavated in the late 19th century, and since then archaeologists have discovered many different styles and changes made in the centuries before the eruption.

References:
Campanero et al: Remodeling the local Pompeian space by combining virtual reality-based eye tracking and a 3D GIS. Antiquity, 2022. DOI:

“Explorer. Unapologetic entrepreneur. Alcohol fanatic. Certified writer. Wannabe tv evangelist. Twitter fanatic. Student. Web scholar. Travel buff.”




