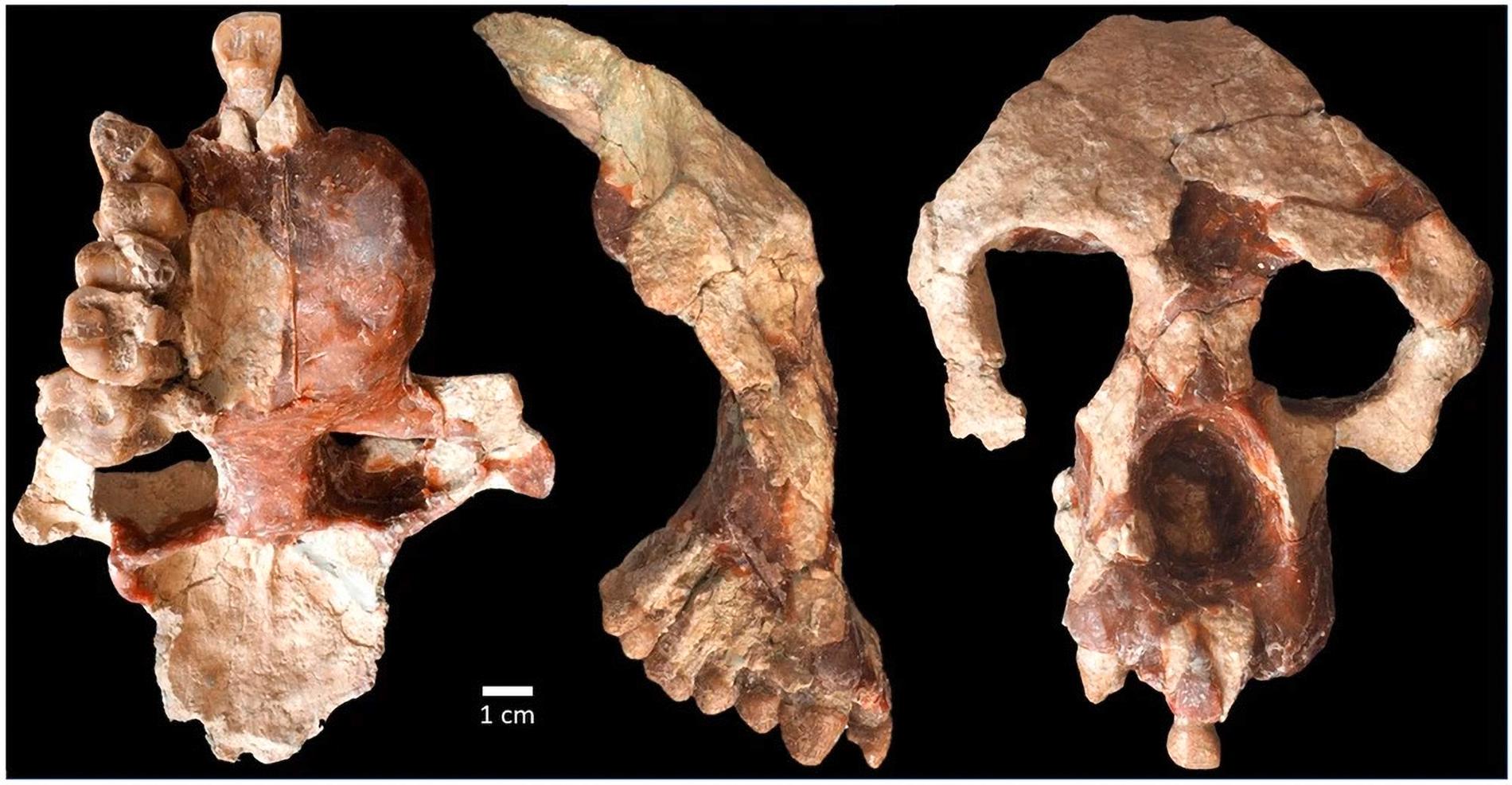
The results of a study on a well-preserved skull from a fossil ape contradict the view of many about apes and human development.
- Researchers from the University of Toronto and the University of Ankara conducted a study on a well-preserved fossil ape skull, according to The Telegraph and SciTechDaily.
- The fossil discovered in Turkey challenges the traditional belief that apes and humans evolved exclusively in Africa.
- The study supports the hypothesis that the ancestors of African apes and humans may have evolved in Europe and later migrated to Africa between 7 and 9 million years ago.
- The fossil is of the species Anadoluvius turkae, which would have been about the size of a large chimpanzee and ate tough or tough food from wild sources.
- The findings suggest that hominins may have evolved in western and central Europe and spread to the eastern Mediterranean before eventually spreading to Africa, but more research and more excavations are needed for confirmation.
The telegraph He writes that the discovery of the fossil ape is rewriting human history.
The researchers believe that the findings from the study of the fossil remains contradict the view that African apes and humans evolved exclusively in Africa.
According to the discovery of the skull Scitec Daily After it was made in Türkiye.
The findings from the skull study should support the hypothesis that the ancestors of African apes and humans may have evolved in Europe and later migrated to Africa between 7 and 9 million years ago.
It has been rewritten in a study conducted by researchers from the University of Toronto and Professor Ayla Sevim Erol at Ankara University. It is posted in Communication biology.
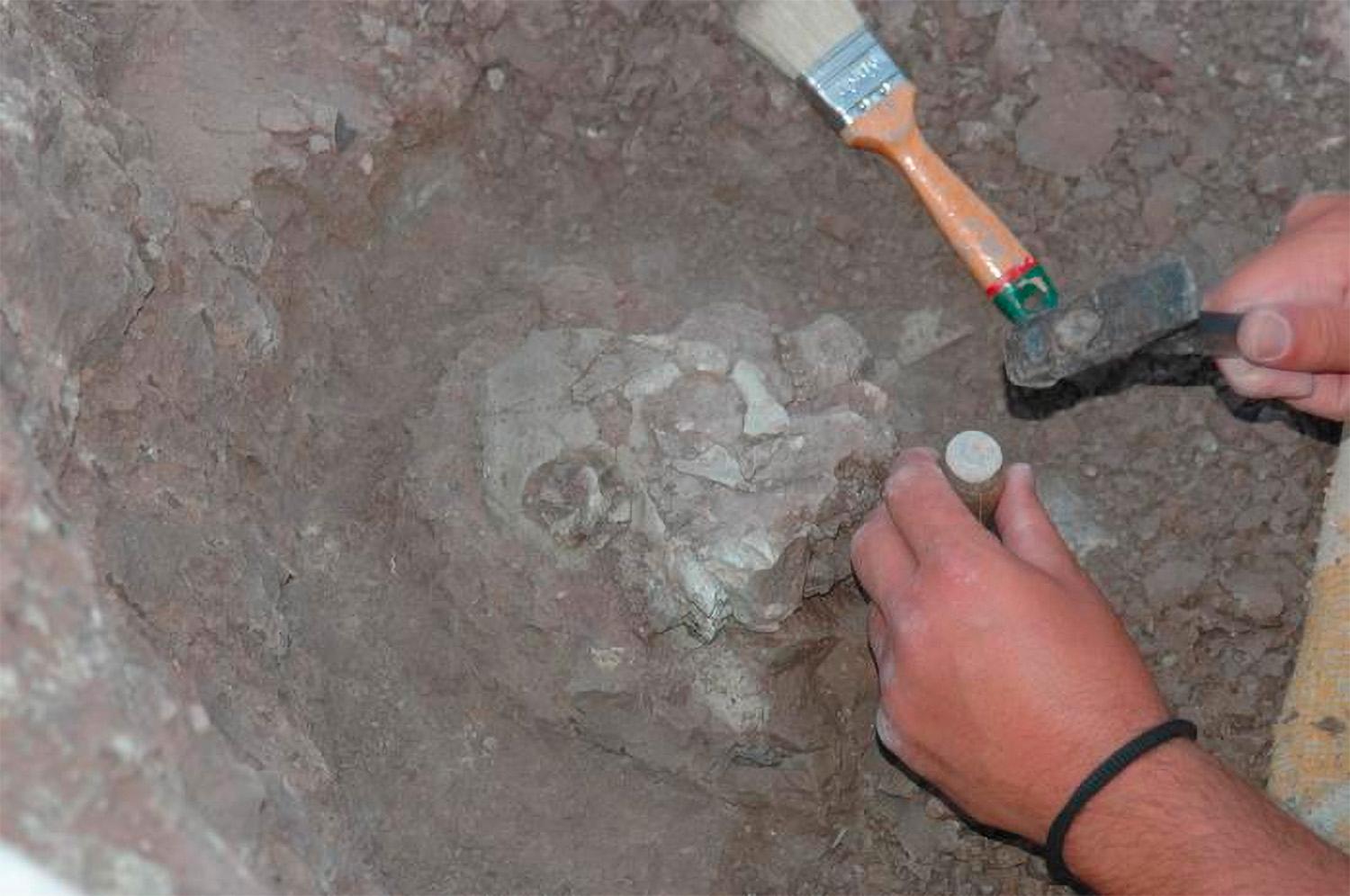

About the size of a large chimpanzee
The conclusion is based on analysis of a well-preserved partial skull discovered in Turkey in 2015.
According to David Begin, a professor in the Department of Anthropology at the University of Toronto, it was the “completeness” of the fossil that allowed them to perform a broader and more detailed analysis. They used software designed to calculate evolutionary relationships.
The fossils described earlier don’t contain much of the skull, he told SciTechDaily.
According to the researchers, the species they found is called Anadoluvius turkae.
According to them, it must have been the size of a large chimpanzee, weighing around 50 to 60 kilograms. They must have lived in dry forests, and must have been on the ground a lot in “open conditions” – unlike what live monkeys do, according to Professor Sevim Erol.
It suggests that they lived in environments similar to those of early humans in Africa.
– Strong jaws and large teeth with thick enamel indicate a diet that includes hard or tough foods from terrestrial sources such as roots and rhizomes.
According to the researchers behind the study, the findings should prove that Anadoluvius turkae is an offshoot of the part of the evolutionary tree that gave rise to chimpanzees, gorillas, and humans.

Fossil apes from the eastern Mediterranean are of central importance to the debate about African apes and humans. (homins)(homins)Hominins are species in the primate family Hominidae that are the direct ancestors of humans as well as humans themselves. Members of the family Hominidae, also called hominids, also include hominins, but the latter is reserved for species that are ancestors, rather than offshoots, of the human family tree Origin,” is written in the study.
Our findings also indicate that not only did humans evolve in western and central Europe, but they spent more than five million years evolving there and spreading to the eastern Mediterranean before eventually spreading to Africa, possibly as a result of changing environments and reduced forests, says Pigeon. Scitec Daily.
And stresses that this does not prove it. More excavations and more research are needed to make this happen.

“Explorer. Unapologetic entrepreneur. Alcohol fanatic. Certified writer. Wannabe tv evangelist. Twitter fanatic. Student. Web scholar. Travel buff.”