We humans search for life in space. If creatures elsewhere did the same thing, could they see the structures made by humans on Earth?
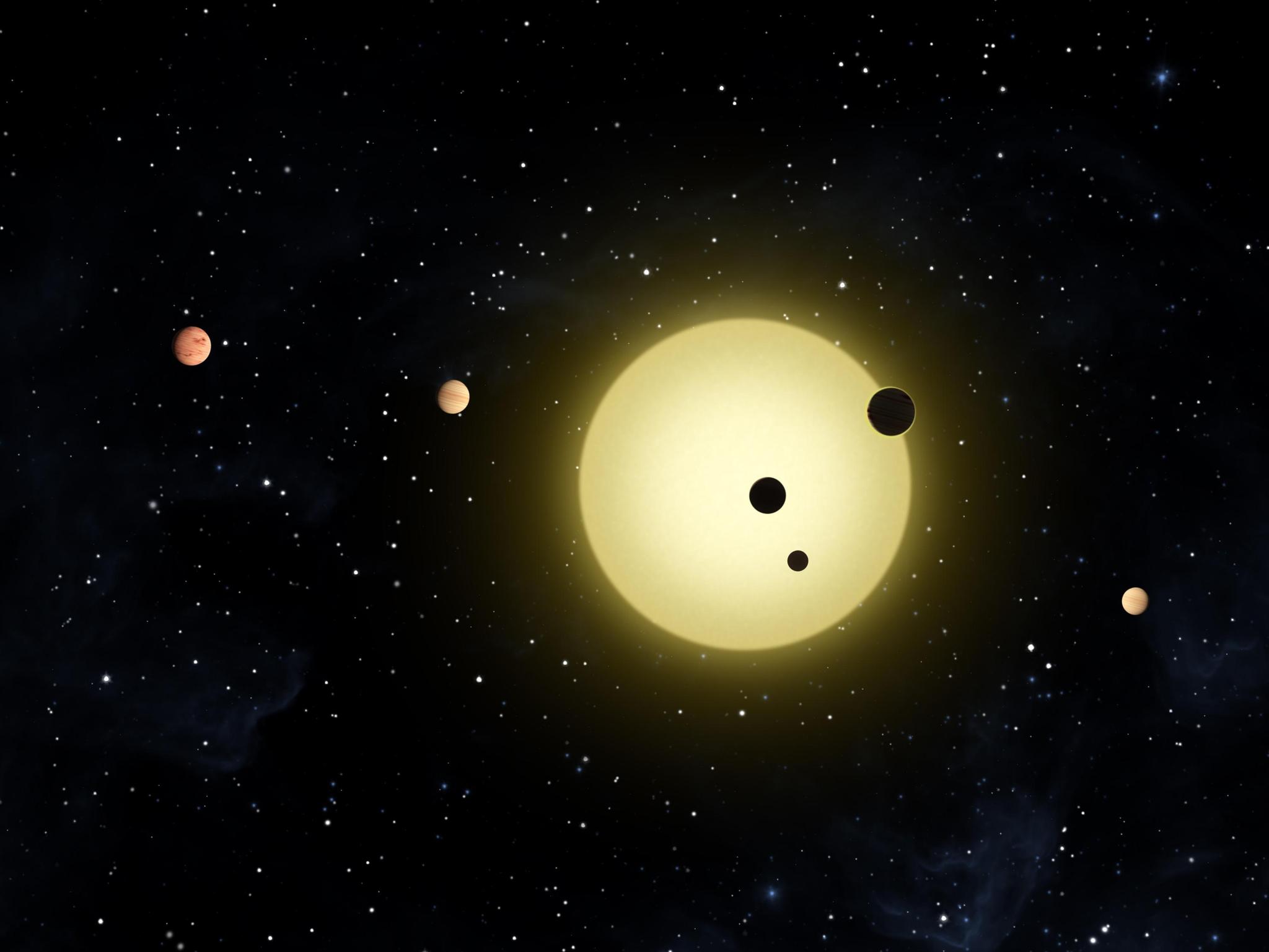

NASA illustration of six exoplanets orbiting the sun-like star Kepler-11. The system is located 2,000 light-years from Earth.
The answer depends on how advanced they are. How far away do they live? This is the opinion of a group of researchers, led by Zaza Usmanov. He is a professor of physics at Tbilisi Free University in Georgia. The report will be published in March in a recognized scientific journal Acta AstronauticaActa AstronauticaA peer-reviewed scientific journal covering astronomy and astrophysics. It was founded in 1925 by a Polish astronomer..
Astronomers on Earth are looking even further into space. Space telescopes have allowed scientists to make tremendous progress in exploring the world inside and outside our galaxy, the Milky Way.
It was not so long ago that planets orbiting distant suns (stars) were pure fantasy. But within a few decades, our view of the world has changed. Observations of the first planets outside our solar system, called exoplanets, were confirmed in the 1990s.
So how much have we found so far?
Away from the neighbour
This is the situation as of January 9, 2024:
- Number of confirmed exoplanets: 5,566.
- Number of unconfirmed exoplanets so far: 10,059.
- Number of confirmed solar systems: 4145.
(Development can be monitored continuously at NASA On this page)
Here we are talking about the planets in our galaxy. The first planet in another galaxy was discovered in 2021. But it is, in any case, so far away (28 million light-years) that there won't be much motion you can pick up by looking at the light from Earth.
Why?

A time-lapse composite image taken over a 17-year period of the massive exoplanet Beta Pictoris b orbiting the star Beta Pictoris b. The system is 63 light-years away from us, and the planet is 46% larger, with a mass of 13 times that of Jupiter.
Slow light
Yes, because the light actually takes a long time to arrive. The speed of 300 thousand kilometers per second may seem fast, but it may seem like the speed of a snail in the giant universe. The diameter of the Milky Way Galaxy is 100 thousand light years. Its nearest neighbor is the Andromeda Galaxy. It is 2.5 million light years away from us. Therefore, it takes 2.5 million years for light to reach it.
This means that if someone observing Earth would be able to see something created by humans, it cannot be very far away. For example, the pyramids were built for approx. 4000 years ago.
But is there life elsewhere?
Life or not?
If so, is it particularly widespread? If so, is it intelligent life?
So far there is no evidence of life anywhere other than Earth. We ourselves at least believe that we have intelligence.
So the researchers' starting point was: If intelligent beings exist, can they detect us and the constructions we've made? How advanced would a civilization have to be that could monitor us? How high can they be at most?
They therefore used a method to measure the technological level of a civilization based on how much energy it was able to use.
it's called Kardashev scaleKardashev scaleDeveloped by Russian astrophysicist Nikolai Kardashev (1932-2019). It divides civilizations into three groups:
Type 1
This type of civilization harnesses the energy equivalent of all the solar energy that reaches the surface of their planet. Researchers believe that such a civilization would be unable to create a telescope powerful enough to see us.
Type 2
A Type II civilization has access to all the energy of the entire star. Such civilizations may be able to observe us from hundreds or thousands of light-years away. But there are probably fewer of them. But if one were found a few thousand light-years away, it would be able to see human activity. For example, the construction of the pyramids in Egypt.
The researchers concluded that the maximum distance at which a 10-meter-high structure could be detected would be 3,000 light-years for such a civilization.
What about type 3? What about us?
The researchers did not include the third group. Type III civilizations are so advanced that they can harness all the energy in the entire galaxy.
For your information: We humans will not reach the first group in this century, according to the expectations of Kardashev himself and other theorists.

“Explorer. Unapologetic entrepreneur. Alcohol fanatic. Certified writer. Wannabe tv evangelist. Twitter fanatic. Student. Web scholar. Travel buff.”