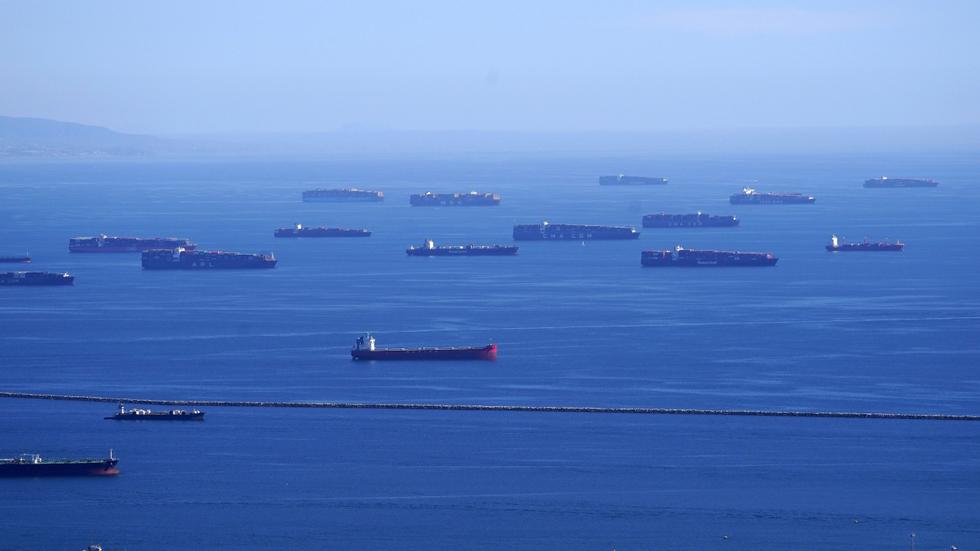
In 2020, new regulations came out from the United Nations International Maritime Organization (IMO) to reduce emissions from shipping.
The new rules according to Science Journal Reduce ship sulfur pollution by more than 80 percent and improve air quality around the world.
But they also created a very small climate paradox: because now scientists have discovered that strange clouds from ship emissions have a very special effect on Earth.
By reflecting sunlight, they help cool the planet.
This is how they look:

Clouds are called “ship tracks” in English Photo: NASA/Reuters/NTB
Going the wrong way
“We’re changing the clouds,” says Duncan Watson-Parris of the new emissions rules, according to Science Magazine, which discusses the issue in its latest issue. Watson-Parris is an atmospheric physicist at the Scripps Institution of Oceanography.
in Stady He and his colleagues concluded that pollution from ship traffic can affect clouds to have a cooling effect nearly twice as strong as previously calculated.
The article continues below the advertisementThe article continues below the advertisement
His research team However, find out Some clouds – altocumulus – have not changed much since the IMO rules came into effect.
own clouds
If you imagine ship traffic at sea, the first thing that comes to mind is probably the ocean and the ship.
What you may not have thought of is that ships usually release sulfate or salt particles that rise into the sky.
Perhaps unknown is that this emission actually affects clouds.
Very simplified, the low clouds that follow the ships are created and brightened by the sulfate particles from the ships, which allow the vapor to condense into numerous, small droplets. This makes it bright and reflective.
Atlantic Ocean
Another researcher, Tianli Yuan, at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, is researching the same phenomenon.
– This year has been crazy.
This is how he describes the situation at sea at the moment. He and his colleagues recently released a study on the effect of these clouds.
The article continues below the advertisement
(article continues below image)

Researchers at NASA study clouds that follow the movement of ships. Image: NASA/AFP/NTB
The research article, which is currently undergoing peer review according to Science, claims that new IMO regulations, which have significantly reduced emissions from ships, have simultaneously contributed to global warming by 0.1 watts per square metre.
Yuan tells Science that fewer clouds as a result of lower emissions are responsible for much of the warming of the Atlantic Ocean this summer.
The North Atlantic is a popular shipping route for ships, and although there have long been warnings of rising sea temperatures, never before has this sea region warmed at the same pace as other sea regions.
But now it’s serious here.
Last month, it was record hot, with 25 degrees on the surface, according to Science.
(Article continues below image).

The Atlantic Ocean is warming. Photo: Shutterstock/NTB
pointing in the same direction
Findings from a third research project, led by Florida State University researcher Michael Diamond, support the findings of Yuan and his research team.
The article continues below the advertisement
Science writes that by examining an expanse of sea in the southeastern Atlantic, it was observed that the size of droplets in clouds had increased by far to the largest size in two decades after emissions fell. in Research article As of July, Diamond calculates that IMO rules have contributed to global warming.
(Article continues below image).

Reducing ship emissions has improved air quality globally, but it has had unexpected side effects. Illustrative photo of Jakarta. Photo: Bay Ismoyo/AFP/NTB
Moving forward, the task will be to gather experience from the many researchers studying this. According to Science, Diamond, Yuan, and other researchers will begin a mission to compare results later this year, under the auspices of National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration in the US Department of Commerce.
Possibility
Researching clouds is complex, but scientists see the lessons learned from this unfortunate development as an opportunity, says Science.
Now, for example, researchers are investigating the idea that ships in the future could create such special clouds by shooting salt particles into the air to create more reflective clouds.
Diamond believes clear evidence has been found that humans can cool the planet by influencing clouds.
— and he strongly suggests that if you want to do it on purpose, you can do it, he tells Science.

“Explorer. Unapologetic entrepreneur. Alcohol fanatic. Certified writer. Wannabe tv evangelist. Twitter fanatic. Student. Web scholar. Travel buff.”